- 27-09-2024
- LLM
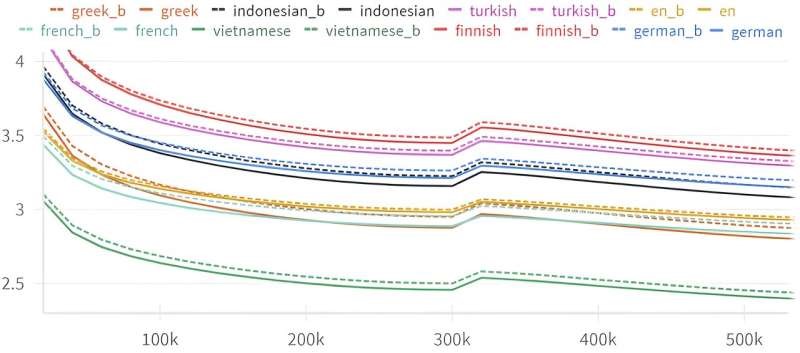
Researchers found that large language models showing greater accuracy in predicting the next word in a sentence than the previous one, revealing an "Arrow of Time" effect in language.
Researchers from EPFL have discovered that large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, exhibit an "Arrow of Time" effect, showing greater accuracy in predicting the next word in a sentence than the previous one. This fundamental asymmetry, observed across various LLM architectures, suggests that while both forward and backward predictions should theoretically be equally challenging, LLMs are consistently a few percent less accurate when predicting backwards. The findings connect to Claude Shannon's work on information theory and imply deeper insights into language structure, intelligence, and even the nature of time. The study originated from a collaboration with a theater school to create a chatbot for improv, leading to unexpected revelations about language processing and causality.